Briefly Describe the Four Phases of the Immune Response
The vascular phase in which blood vessels dilate open and tissues swell to accommodate the rapid influx of immune cells and antimicrobial chemicals What is chronic inflammation. First week only 499.

Immunity And Infection Ppt Download
Allergies involve an immune response to a substance that most peoples bodies perceive as harmless.
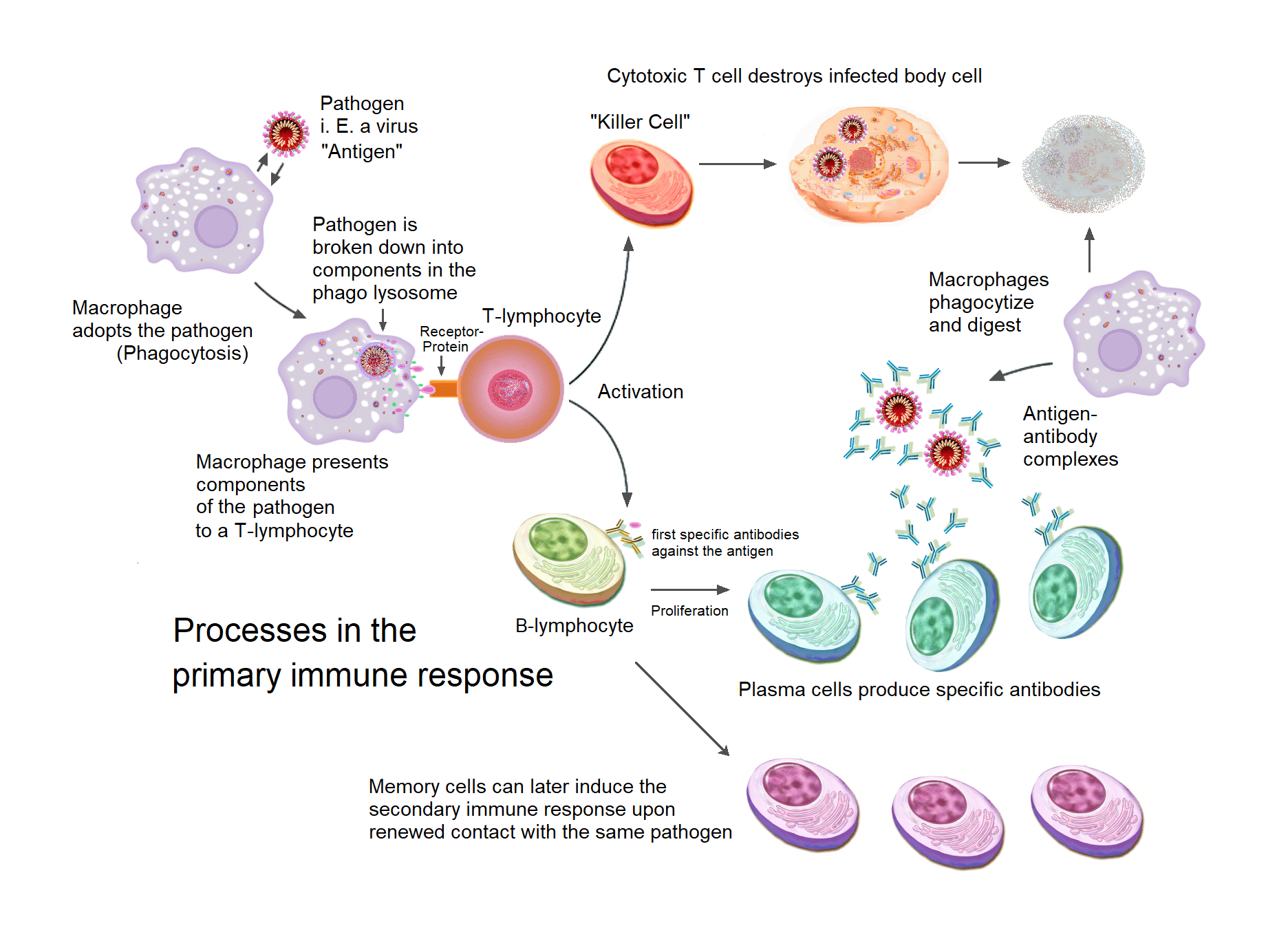
. Effect Responses of Humoral Immunity. Antrum is basically the fluid filled cavity that has a great role in a transition phase from the pri. The innate general immune system and the adaptive specialized immune system.
An immune response is generally divided into innate and adaptive immunity. A virus infected cell. Primary.
Given the four stages of syphilis and describe the symptoms. An intracellular pathogen sequestered inside a macrophage. Unlike other antibodies it does not actively circulate but instead binds to B cells to instigate the immune response.
Cell signaling can be divided into 3 stages. Name three general types of laboratory tests useful in the diagnosis of syphilis. Detection of DTH.
The pathogen bypasses barrier defenses and starts multiplying in the hosts body. Phases of DTH response. B Immune complex formation.
In the figure below trace the flow of lymph in four stages. An extracellular viral or bacterial pathogen or an extracellular exotoxin. As a signaling antibody IgD helps incite the release of front-line IgM to fight disease and infection.
Vaccination immunization is a way to trigger the immune response. However they usually act together with the innate response representing the first line of host defense and with the adaptive response becoming prominent after several days as antigen-specific T and B cells have undergone clonal. The main parts of the immune system are.
A cell detects a signaling molecule from the outside of the cell. Briefly describe the procedure for the RPR VDRL FTA-ABS TPI and microhemagglutination tests. Cytokines in DTH.
The T cell response can be suppressed by all of the following except. Refer to picture arrow_forward. The lymphatic system for most people is associated with the immune system to such a degree that the two systems are virtually indistinguishable.
Start your trial now. Explain the role of the following two antimicrobial compounds. Immune memory follows the adaptive response when mature.
Features of an Immune Response. The immune system fights germs and foreign substances on the skin in the tissues of the body and in bodily fluids such as blood. C method of inducing autoimmunity.
Innate immunity occurs immediately when circulating innate cells recognize a problem. These are the parts of your immune system that actively fight infection. And 3 memory the ability to recognize and mount an enhanced response against the same antigen on subsequent.
Solution for briefly describe the cell elongation in response to auxin close. Hemolytic plaque assay. Describe the plants response to the presence of light.
Small doses of an antigen such as dead or. 2 amplification the ability to develop an enhanced response on repeated exposure to the same antigen. The task of identifying these factors that regulate our immune system has become the main challenge facing precision medicine a proposed medical model aimed at offering patient treatments tailored to individual needs.
B defect in the cell-mediated immune system. For each stage explain the role of the lymphatic system in innate defense. Adaptive immunity occurs later as it relies on the coordination and expansion of specific adaptive immune cells.
The first arrow shows exposure to antigen A. Regulation of Immune Effector Response. During the first 4 to 5 days the innate immune response will partially control but not stop pathogen growth.
Immune proteins like acute phase proteins like complement and antibodies bind to the surface of bacteria by a process called opsonisation. As the adaptive immune response gears up however it will begin to clear the pathogen from the body while at the same time becoming stronger and stronger. In this response activated T cells differentiate and proliferate becoming Helper T H cells or Cytotoxic T C cells.
Our age sex infection history and genetics can affect our immune system and make us more prone to disease. Immune response to infection. These two systems work closely together and take on different tasks.
The innate and adaptive immune systems are often described as contrasting separate arms of the host response. During the first 4 to 5 days the innate immune response will partially control but not stop pathogen growth. Antigen mediated regulation.
Encounter activation attack and memory. Immunoglobulin D IgD is important in the early stages of the immune response. Describe in a step-by step fashion the specific immune systems response to.
Immune system disorders occur when the immune response is directed against body tissue is excessive or is lacking. Opsonised bacteria are therefore coated with molecules that phagocytic cells recognise and respond to. The immune system is the complex collection of cells and organs that destroys or neutralizes pathogens that would otherwise cause disease or death.
If the defense is. Activated phagocytes engulf and destroy opsonised bacteria by a process called phagocytosis. The adaptive immune response in B cells Helper T cells and Cytotoxic T cells involved four phases.
Primary and secondary immune response. As the adaptive immune response gears up however it will begin to clear the pathogen from the body while at the same time becoming stronger and stronger. E Antibodies against CD3.
The immune response is characterized by 1 specificity ie reactivity is directed toward and restricted to the inducing agent termed the antigen. Chronic inflammation is inflammation that persists for months or years typically as a result of a chronic condition like diabetes heart disease COPD or HIV. Briefly describe the following features of.
The immune system is made up of two parts. A failure to make any antibodies. When a pathogenic disease-causing microorganism invades the body for the first time the clinical observable response may range from nothing at all through various degrees of nonspecific reactions to specific infectious diseaseImmunologically however there is always a response the purpose of which is defense.
Pathological responses of DTH. A signal is detected when the chemical signal also known as a ligand binds to a receptor protein on the surface of the cell or. Unlike the innate immune system which attacks only based on the identification of general threats the adaptive immunity is activated by exposure to pathogens and uses an immunological memory to learn about the threat.
The pathogen bypasses barrier defenses and starts multiplying in the hosts body. Compare the advantages and disadvantages for the above tests. White blood cells antibodies the complement system the lymphatic system the spleen the thymus and the bone marrow.
The adaptive immune system also called acquired immunity uses specific antigens to strategically mount an immune response.
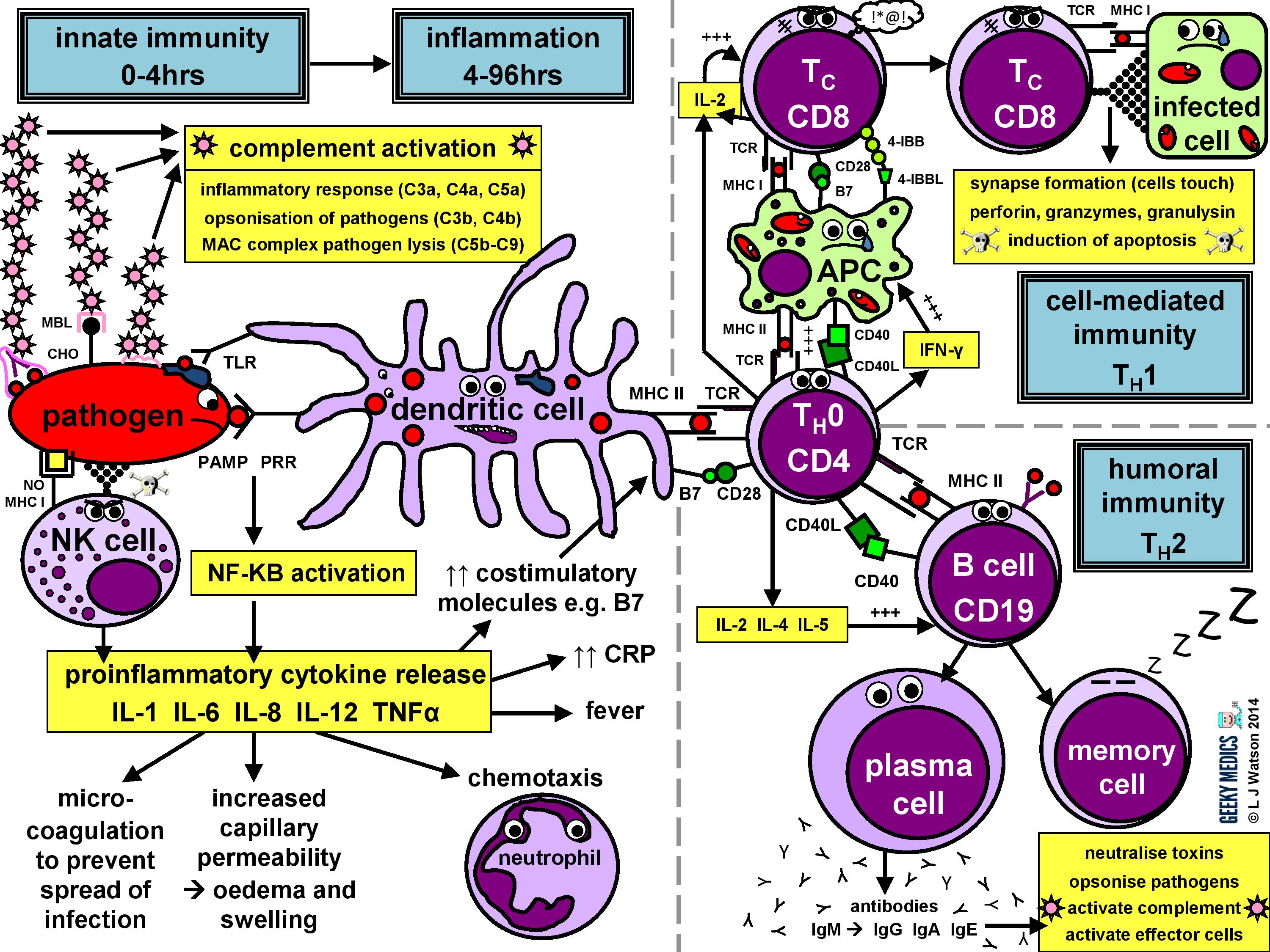
Immune Response Immune Cell Types Geeky Medics
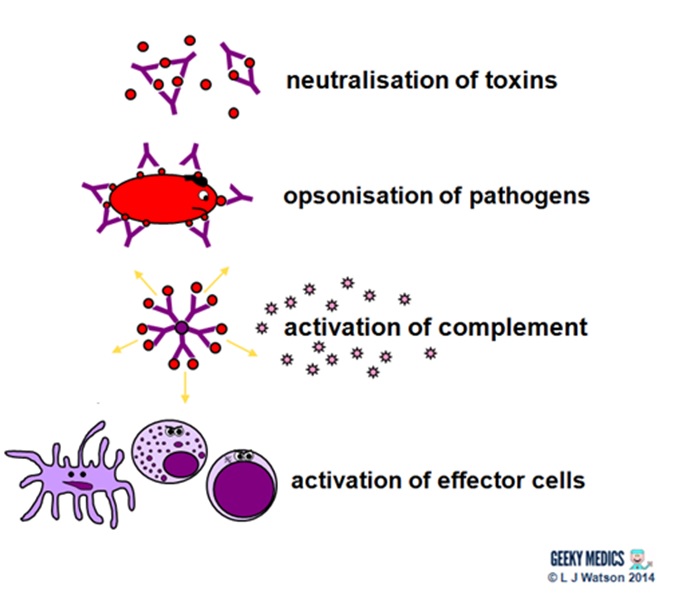
Immune Response Immune Cell Types Geeky Medics

Primary And Secondary Responses Memory Cells Teachmephysiology
0 Response to "Briefly Describe the Four Phases of the Immune Response"
Post a Comment